The Impact of Climate-Responsive Architecture in Bangalore
Read latest blogs and articles from Housystan
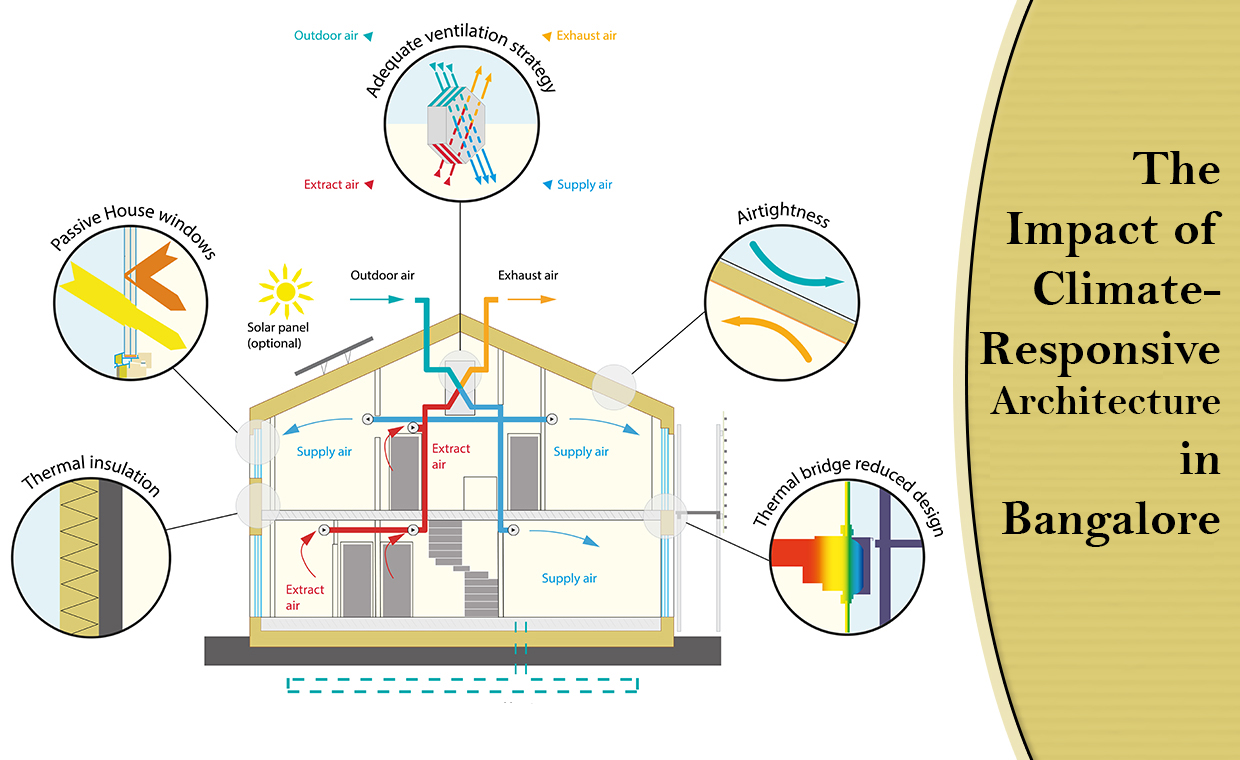
The Information mentioned here was last updated on:
25/2/2026The Impact of Climate-Responsive Architecture in Bangalore
Introduction: Bangalore’s Urban Landscape and the Need for Climate-Responsive Design
Bangalore, often referred to as India’s “Silicon Valley,” has experienced rapid urbanization and population growth over the last few decades. While technological progress has driven the city’s prosperity, it has also led to environmental challenges such as the urban heat island effect, diminishing green cover, and increased energy consumption. In response, the architectural community in Bangalore is turning towards climate-responsive architecture—a design approach that integrates local climate conditions and sustainable principles into building solutions. This movement is not just a trend, but a necessity for creating resilient, energy-efficient, and comfortable urban environments in the face of changing climate patterns.
- Verified Tenants/Buyers
- Unlimited Property Listing
- Zero subscription/charges fee
Understanding Climate-Responsive Architecture
Climate-responsive architecture refers to the practice of designing buildings and spaces that are attuned to the specific climatic conditions of their location. By analyzing factors like solar orientation, wind direction, rainfall patterns, and temperature fluctuations, architects in Bangalore can create structures that naturally regulate indoor environments, reduce reliance on artificial cooling and heating, and minimize environmental impact. The objective is to harmonize built forms with nature, ensuring comfort while maximizing sustainability.
Key Principles of Climate-Responsive Design in Bangalore
Several core principles guide climate-responsive architecture in Bangalore:
1. Passive Cooling Techniques
Given Bangalore’s predominantly warm climate, passive cooling is essential. Techniques include cross ventilation, thermal mass construction, shaded courtyards, and using materials with high reflectivity. Buildings are oriented to capture prevailing breezes while minimizing direct sun exposure, reducing the need for air conditioning.
2. Sustainable Material Selection
Local materials such as laterite stone, terracotta tiles, and fly ash bricks are increasingly favored. These materials reduce transportation emissions and blend seamlessly into the surrounding landscape. They also offer excellent insulation properties, further supporting thermal comfort.
3. Maximizing Natural Light
Strategic window placement, skylights, and light wells allow ample daylight to permeate interiors, reducing the need for artificial lighting. Careful design ensures that natural light is balanced without causing glare or excessive heat gain.
4. Water Conservation Strategies
Rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and permeable landscaping are integral to climate-responsive projects in Bangalore. With the city’s periodic water shortages, these features ensure efficient water management and reduce the burden on municipal resources.
Innovative Examples of Climate-Responsive Architecture in Bangalore
Bangalore is home to several pioneering projects that showcase the potential of climate-responsive design:
The Infosys Campus
The Infosys campus in Electronics City is a model of energy-efficient design. The campus incorporates green roofs, passive cooling corridors, and extensive landscaping. Solar panels and wind turbines contribute to renewable energy generation, while water bodies and shaded walkways lower ambient temperatures.
Good Earth Malhar
Good Earth Malhar, a residential community on the city’s outskirts, focuses on low-rise, earth-friendly homes. The development features mud blocks, shaded verandas, and lush courtyard gardens. Residents benefit from cool interiors and low energy bills, thanks to natural ventilation and insulation.
Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Buildings
The IISc campus integrates climate-responsive elements such as deep overhangs, ventilated facades, and rainwater harvesting systems. These features not only reduce operational costs but also foster a harmonious relationship between built and natural environments.
Benefits of Climate-Responsive Architecture for Bangalore’s Future
Embracing climate-responsive design brings tangible benefits to both the city and its residents:
1. Energy Efficiency and Reduced Carbon Footprint
By minimizing dependence on air conditioning, artificial heating, and lighting, climate-responsive buildings significantly lower energy consumption. This translates into reduced greenhouse gas emissions, helping Bangalore meet its sustainability targets.
2. Enhanced Comfort and Well-Being
Buildings designed with local climate in mind provide superior thermal comfort, better air quality, and abundant natural light. Occupants enjoy healthier, more pleasant living and working environments, contributing to overall well-being.
3. Water Security and Resource Conservation
Innovative water management strategies ensure that buildings make the most of every drop. Rainwater harvesting and recycling reduce dependence on external water sources, building resilience in the face of water scarcity.
4. Economic Advantages
While some climate-responsive features may require higher initial investment, they offer long-term savings through reduced utility bills and maintenance costs. Additionally, properties with sustainable features command higher resale values in Bangalore’s competitive real estate market.
Challenges in Mainstreaming Climate-Responsive Architecture
Despite its advantages, wider adoption of climate-responsive architecture faces several hurdles in Bangalore. These include lack of awareness among homebuyers, higher upfront costs, and regulatory bottlenecks. However, as the effects of climate change become more pronounced, there is growing recognition of the need for resilient and sustainable urban development.
The Role of Policy and Education
Government policies play a crucial role in promoting climate-responsive architecture. Incentives such as tax rebates, fast-track approvals, and green building certifications encourage developers to integrate sustainable practices. Academic institutions are also updating curricula to include climate-responsive design, ensuring that the next generation of architects is equipped to tackle environmental challenges.
The Future: Towards a Climate-Positive Bangalore
As Bangalore continues to expand, climate-responsive architecture will be indispensable in shaping a sustainable future. By blending tradition with innovation, the city’s architects and planners are redefining urban living for the 21st century. The integration of green spaces, renewable energy, and resource-efficient design is not just a blueprint for buildings, but a vision for a thriving, resilient metropolis.
Conclusion: Building Resilience Through Design
Bangalore’s journey towards sustainable urbanization is intricately linked with climate-responsive architecture. As awareness grows and technology evolves, the city is poised to lead by example—demonstrating that thoughtful design and environmental stewardship can go hand in hand. For citizens, developers, and policymakers alike, embracing climate-responsive principles is more than an architectural choice; it is a commitment to a healthier, more sustainable Bangalore for generations to come.